The Ancient Origins of my African Ancestors
The Khoisan:
The Khoisan were early Inhabitants of Southern Africa approximately. 260,000 years ago. The Khoisan, a group representing the indigenous peoples of Southern Africa, are a combination of the Khoekhoen and the San peoples. These ancient populations are believed to have inhabited the region long before the Bantu expansion, which occurred around 1500-2000 years ago. The San people were known as skilled foragers, residing in areas like the Kalahari Desert, as well as regions of Botswana, Namibia, Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Lesotho, and South Africa. The Khoekhoe peoples might have arrived in Southern Africa during the late Stone Age, possibly due to displacement caused by the Bantu migration.
A remarkable feature of Khoisan languages is the abundance of click consonants. Interestingly, the influence of the Khoisan languages extended beyond their own communities, leaving an impact on other languages in the region. Both Xhosa and Zulu languages adopted click consonants, possibly as a result of contact and interaction with the Khoisan populations. The origins of the Khoisan can be traced back as early as 260,000 years ago, making them one of the oldest inhabitants of Southern Africa.
The Bantu:
The Bantu Expansion was a rapid succession migration in Africa around 1000 BC. The Bantu Peoples are a group of individuals who speak languages derived from the Proto-Bantu language, which was spoken around 4000 years ago in West/Central Africa. During the first millennium BC, the Bantu Expansion occurred, leading to a series of rapid migrations. As they moved, Bantu peoples encountered and interacted with earlier inhabitants of central and southern Africa, such as the Pygmy and Khoisan populations. The interactions resulted in assimilation or displacement of these pre-existing groups.
One significant aspect of the Bantu migration was their acquisition of cattle from the Cushitic neighbors. This interaction led to various ethnic admixtures, such as the Tutsi in the African Great Lakes region. In Southern Africa, a prominent clan of Bantu people, known as the Zulu, emerged as a powerful state in 1818 under the leadership of the renowned Zulu King Shaka.
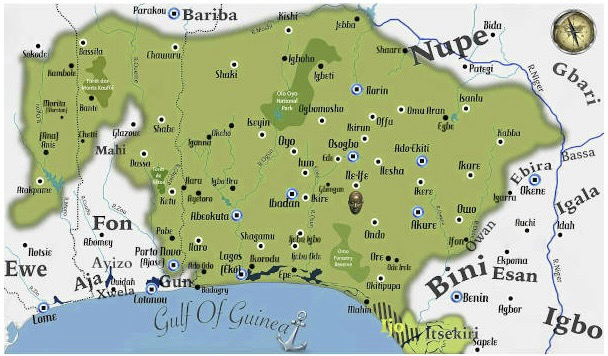
The Yoruba:
The Yoruba people are an African ethnic group inhabiting western Africa. They evolved from earlier Mesolithic Volta-Niger populations by the first millennium BC. As early as the 11th century, the Yoruba had become the dominant cultural force in southern Nigeria. Their society was organized around powerful city-states, exhibiting impressive urban structures and well-structured communities. Even before the arrival of colonial powers, Yoruba cities were known for their fortresses with high walls and gates, ranking among the most populous in Africa.
Archaeological findings indicate that the capital of the Yoruba empire once housed over 100,000 people, demonstrating the extent of their civilization. Present-day Lagos, another major Yoruba city, has a population of over twenty million, reflecting the continuity of their urban legacy. The Yoruba consider the dynasty of kings at Ife-Ife as the origin of human civilization, and this rich cultural heritage remains intact to this day, with Ife-Ife being revered as their spiritual homeland.
Recommend0 recommendationsPublished in Ancestry :stories, BLACK :stories
Responses